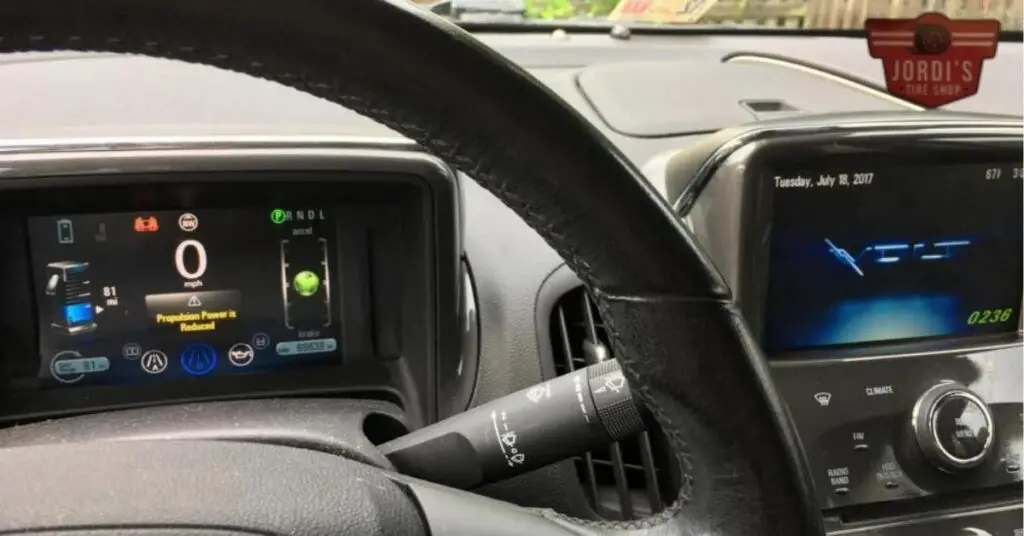
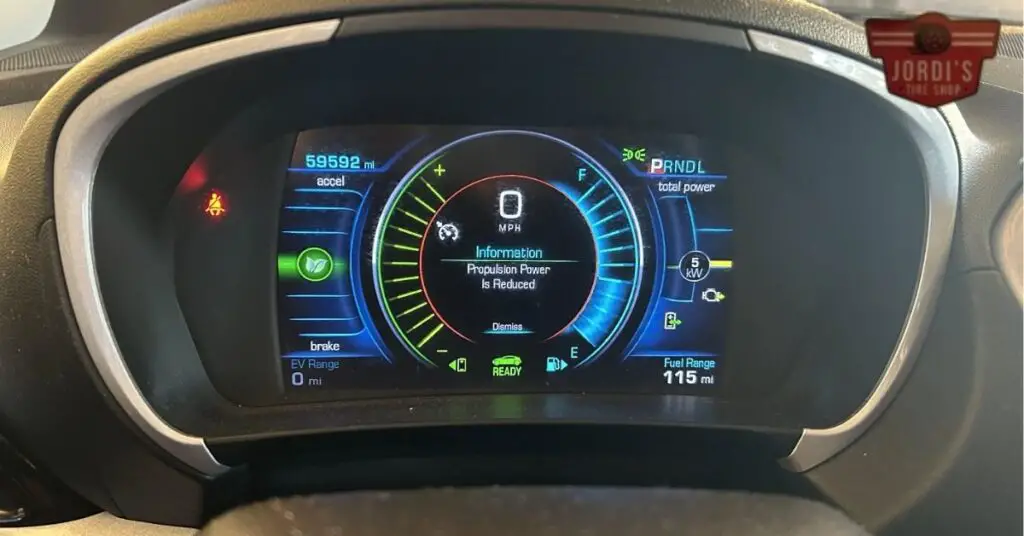
In the world of electric vehicles (EVs), power is everything. It’s what gets us from A to B with the zip and zest we’ve come to love. But what happens when that power starts to wane? We’ve noticed a trend that’s got many EV enthusiasts scratching their heads: a reduction in volt propulsion power. It’s a topic that’s as intriguing as it is important, and we’re here to dive into it together.
Understanding the nuances behind this power reduction can help us navigate the future of electric mobility. Whether you’re a seasoned EV driver or just EV-curious, knowing the ins and outs of what affects your vehicle’s performance is key. Let’s embark on this journey to uncover the mysteries behind the decrease in volt propulsion power and what it means for us, the drivers, in the long run.
Understanding Volt Propulsion Power
Volt propulsion power refers to the electrical force that drives electric vehicles (EVs) forward. This power originates from the vehicle’s battery pack, which supplies voltage to the electric motor, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. Essentially, it’s what moves an EV from point A to point B efficiently and sustainably.
Several factors can lead to a reduction in volt propulsion power, affecting overall vehicle performance. First, battery health plays a pivotal role. Over time, batteries naturally degrade, leading to a decrease in their ability to hold and supply the necessary power. Conditions like extreme temperatures, either too hot or too cold, can also temporarily affect battery performance and, consequently, power output.
Moreover, driving habits significantly impact volt propulsion power. Frequent rapid acceleration and reliance on high speeds demand more power from the battery, leading to quicker depletion of energy reserves. This not only reduces the power available for propulsion but also accelerates battery wear, which could lead to a more permanent reduction in power capability.
Software updates are another influential factor. Manufacturers often release updates that can alter the vehicle’s power management system. While these updates aim to enhance overall efficiency and safety, they can occasionally lead to a perceived decrease in propulsion power, especially if they limit power output to preserve battery life or protect the motor from excessive stress.
Finally, mechanical issues, such as problems with the electric motor or the power electronics, can lead to a decrease in propulsion power. Regular maintenance and checks can help identify and rectify these issues promptly, ensuring the vehicle operates at its optimal performance level.
Common Causes of Reduced Volt Propulsion Power
Building on our understanding of the significance of volt propulsion power and its impact on electric vehicle (EV) performance, let’s explore the common causes of reduced power in more detail. Understanding these factors can help EV owners maintain their vehicles more effectively.
- Battery Health Deterioration: Over time, the battery’s ability to hold a charge diminishes, leading to reduced propulsion power. Factors such as age, the number of charge cycles, and exposure to extreme temperatures contribute to this deterioration.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both very cold and very hot temperatures affect the battery’s performance. In cold weather, batteries can’t release their stored energy as efficiently, and in hot weather, the battery may overheat, leading to reduced power output.
- Drive System Mechanical Issues: Components within the drive system, such as the electric motor or transmission, can wear out or malfunction, impeding the vehicle’s propulsion power. Regular maintenance helps identify these issues early.
- Software Updates: Occasionally, software updates aimed at improving vehicle performance or fixing existing bugs can inadvertently reduce propulsion power. Staying informed about updates and their impacts can help owners seek necessary adjustments.
- Inadequate Charging Infrastructure: Inconsistent or insufficient charging can lead to incomplete power restoration, directly affecting propulsion power. Using manufacturer-recommended chargers and following best charging practices ensures the battery charges fully and efficiently.
- Driving Habits: Aggressive driving, including rapid acceleration and heavy braking, can drain the battery more quickly than smooth, consistent driving. Adopting eco-friendly driving habits can help conserve propulsion power.
Diagnosing Reduced Volt Propulsion Power
Diagnosing reduced volt propulsion power in electric vehicles (EVs) entails a structured approach to pinpoint the exact cause or causes affecting the vehicle’s performance. Through our exploration, we identify key procedures and tools to effectively diagnose issues leading to decreased propulsion power.
Identifying Symptoms
First, noting specific symptoms is vital. Signs such as slower acceleration, limited top speed, or the display of error messages on the dashboard can all indicate reduced propulsion power. These symptoms guide us towards understanding whether the problem is with the battery, the electrical systems, or the mechanical components of the vehicle.
Consult Diagnostic Tools
Next, using diagnostic tools is crucial for accurate detection. Most EVs, including the Volt, come equipped with advanced onboard diagnostic systems (OBD-II) that can generate codes pointing to the malfunctioning parts of the vehicle. Scanning these codes with a compatible OBD-II scanner provides insights into potential issues with the propulsion systems.
Battery Health Inspection
Examining the battery health follows as a critical step. This involves checking the battery’s state of charge, its capacity for holding charge, and any signs of deterioration. For this, specialized battery management system (BMS) diagnostic tools are essential, as they can assess the battery’s condition and predict its remaining lifespan.
Checking for Software Updates
Verifying the vehicle’s software is up to date is also key. Manufacturers often release software updates that can enhance the vehicle’s performance or fix known issues that may be causing reduced propulsion power. Ensuring the vehicle’s software is current can sometimes resolve these performance issues without the need for further mechanical intervention.
Inspecting Mechanical Components
Lastly, inspecting the mechanical components, like the electric motor and drivetrain, confirms there aren’t any physical obstructions or damages causing the reduced power. This might involve visual inspections and tests of the motor’s efficiency under various loads.
Solutions and Maintenance
Recognizing the critical role of volt propulsion power in electric vehicles (EVs) leads us to explore solutions and maintenance practices essential for optimizing performance. Based on the diagnosis of reduced propulsion power, we outline several corrective actions and preventive maintenance strategies.
Regular Battery Conditioning
- Perform Scheduled Conditioning: Extend battery life and maintain power output by adhering to the manufacturer’s conditioning schedule. Conditioning helps balance the battery cells and improve their efficiency.
- Manage Charging Practices: Avoid letting the battery drain completely. Aim for charging sessions before the battery level drops below 20%. Additionally, limit frequent full charges to 100% to reduce wear.
Software Updates and Calibration
- Stay Updated with Firmware: Software plays a significant role in managing volt propulsion power. Ensure the vehicle’s firmware is up to date, taking advantage of improvements and bug fixes that directly impact propulsion efficiency.
- Calibrate Systems Regularly: Sensor calibration is crucial for accurate propulsion control. Schedule regular calibration checks to ensure sensors accurately reflect vehicle performance and battery health.
Mechanical Inspections and Repairs
- Inspect Critical Components: Pay attention to wear and tear on mechanical parts such as electric motors and gearboxes. Regular inspections can pinpoint issues before they escalate, preserving propulsion power.
- Replace Worn Parts Timely: Proactive replacement of components like brake pads, bearings, and other drivetrain parts can prevent added stress on the propulsion system, ensuring smoother operation and sustained power output.
- Moderate Acceleration: Sudden acceleration can strain the propulsion system. Adopting smoother acceleration patterns can enhance battery performance and propulsion power over time.
- Utilize Eco Modes: Many EVs offer driving modes optimized for efficiency. Engaging eco modes adjusts vehicle dynamics for maximum energy conservation, indirectly supporting propulsion system longevity.
Case Studies: Vehicles Affected by Reduced Volt Propulsion Power
After discussing the importance of maintaining volt propulsion power in electric vehicles (EVs) and outlining strategies to optimize performance, let’s delve into real-world applications through case studies. These examples demonstrate the impact of reduced volt propulsion power on various vehicle models and highlight the effectiveness of our suggested maintenance practices.
- Chevrolet Bolt: Owners have reported instances where the vehicle displayed a “Propulsion Power is Reduced” message, leading to noticeably slower acceleration. A common cause identified was battery health, particularly in vehicles subjected to frequent fast charging or operated in extreme temperatures. By following battery conditioning practices and software updates recommended by Chevrolet, many owners saw improvements in propulsion performance.
- Nissan Leaf: Some Leaf models experienced reduced power due to aging battery cells. These vehicles, especially those from the early 2010s, showed a decline in range and power over time. Nissan’s approach involved offering battery replacements and software updates to manage battery health more efficiently. This case underscores the importance of battery maintenance for sustaining propulsion power.
- Tesla Model S: While less common, the Model S faced propulsion power issues primarily due to software glitches. These instances typically occurred after major updates and affected the vehicle’s acceleration. Tesla addressed the problems through subsequent software patches and advised owners on recalibrating sensors and managing driving habits to prevent recurrence.
- BMW i3: The i3’s reduced propulsion power issues were often linked to mechanical malfunctions, such as issues with the electric motor or the range extender. BMW’s solution included mechanical inspections and repairs, complemented by software updates to prevent similar issues. This highlights the need for regular mechanical checks alongside electronic maintenance.
Through these case studies, we see how different factors contribute to reduced volt propulsion power in EVs. They also illustrate the effectiveness of combining regular maintenance, software updates, and changes in driving habits to ensure optimal performance and longevity of electric vehicles.
Conclusion
We’ve journeyed through the intricacies of maintaining volt propulsion power in EVs, understanding the pivotal role of battery health, temperature effects, and driving habits. Through various case studies, from the Chevrolet Bolt to the BMW i3, we’ve seen how software updates, regular maintenance, and mindful driving can significantly enhance EV performance and longevity. Let’s embrace these insights, ensuring our electric journeys are not only sustained but also optimized for the future. Here’s to smoother drives and more efficient vehicles on our roads!
Related Posts:
- Best Winter Tires for Honda Civic: Top Picks for Safe and Smooth Driving in Cold Weather
- Check Engine Light Goes Off By Itself: What It Means and What to Do
- Difference Between Tire and Wheel: A Simple Explanation
- Volt Propulsion Power Reduced: Causes and Solutions
- F150 Blend Door Actuator Reset: Quick and Easy Steps
- Supercharged Scat Pack: The Ultimate Muscle Car Upgrade
- Sys Off to Save Battery: Simple Tips to Extend Your Device’s Battery Life
- Suspension Tuning Car: Tips for Improving Your Ride Quality
- Gear Ratio by VIN: How to Find It for Your Vehicle
- Engine Wash: How to Keep Your Vehicle Running Smoothly