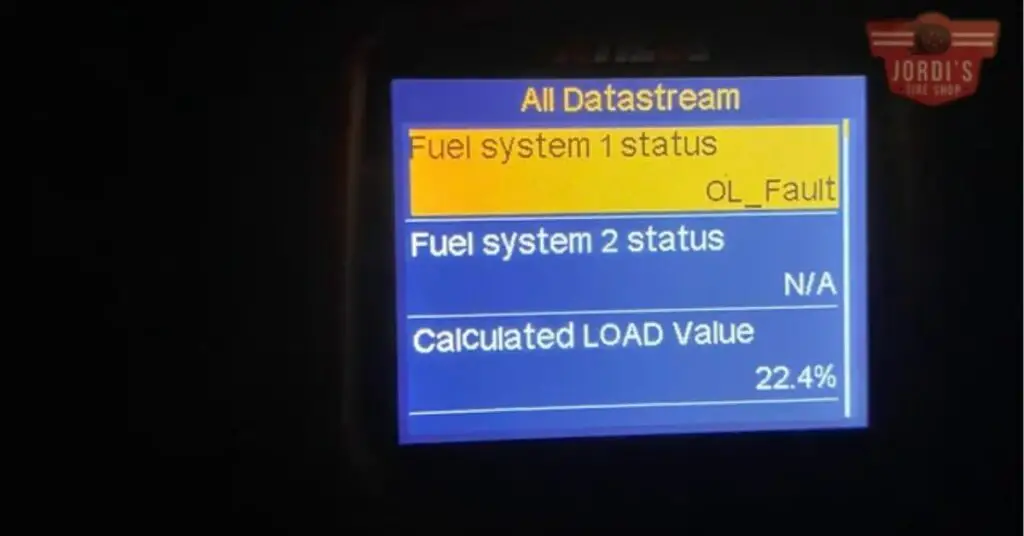
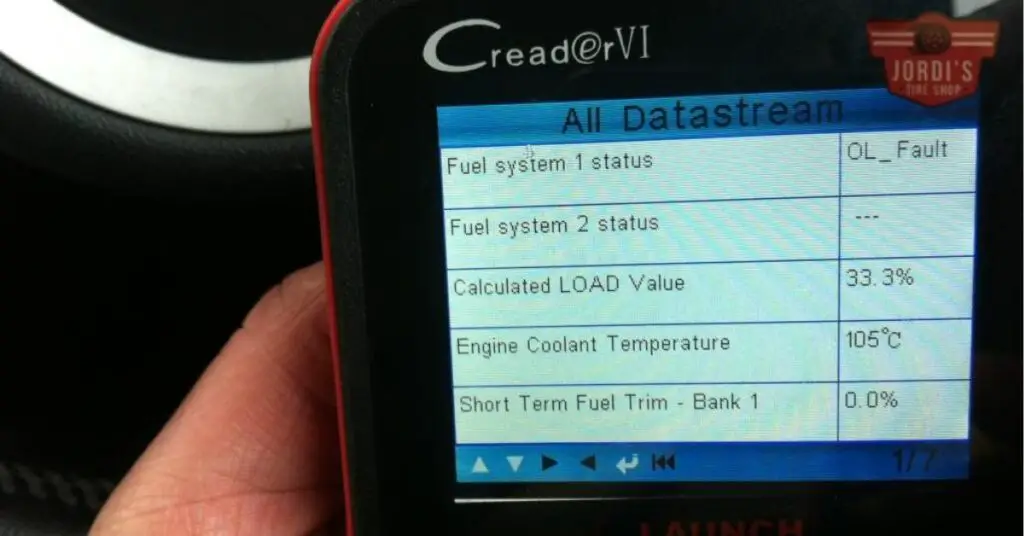
Ever found yourself puzzled by the “fuel system 1 ol fault” warning light flashing on your car’s dashboard? You’re not alone. This cryptic message has left many motorists scratching their heads, unsure of what it means or how serious it might be.
In the industry of cars, few things are more frustrating than an unexpected fault. But don’t panic. Understanding these alerts can be your first step toward resolving them. We’re here to demystify this particular fault and guide you on what to do next.
So, buckle up! As we navigate the ins and outs of the “fuel system 1 ol fault”, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to handle this common car hiccup with confidence. Let’s hit the road to a more informed and worry-free driving experience.
Understanding the Fuel System 1 OL Fault
Exploring into the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault,’ let’s unravel its definition, meaning, and the fuel system’s importance in a vehicle.
Definition and Meaning of Fuel System 1 OL Fault
Unscrambling the term ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’, it’s indicative of a performance issue in your vehicle’s fuel management system. When your car exhibits this fault, it signifies that the fuel system is operating in an ‘open loop’ status, a condition typically triggered by an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture. Notably, the ‘1’ in this fault message represents bank 1 of the engine, alluding to the side of the engine containing cylinder 1.
The term ‘open loop’ refers to situations when the engine control unit (ECU) stops regulating the air-fuel mixture based on feedback from oxygen sensors. Instead, it determines the mixture based solely on preset values. Generally, engines operate in an open loop when they are warming up or under heavy load but shifting to this mode due to a malfunction can lead to efficiency issues and higher emissions.
Importance of Fuel System in a Vehicle
Highlighting the fuel system, it’s the lifeline of your vehicle. This intricate arrangement is devised to store, supply, and mix fuel with air to power the engine. Primely, it comprises of three parts: the fuel tank, the fuel pump and the carburetor or fuel injectors. Each component serves a critical role in the entire operation.
The fuel tank stores the gasoline, the fuel pump transfers it from the tank to the engine and the carburetor or fuel injectors merge the fuel with air to create the combustible mixture that powers your vehicle. Hence, any malfunction, as indicated by a ‘fuel system 1 ol fault,’ can disrupt this equilibrium, severely affecting vehicle performance. Recognizing these faults promptly and seeking professional help can go a long way in managing these vehicle issues.
Symptoms of Fuel System 1 OL Fault
Understanding the symptoms associated with the fuel system 1 OL fault helps in recognizing the issue quickly, enabling prompt action.
Noticeable Indicators Under Normal Vehicle Use
Distinct signs often emerge when using the vehicle under normal conditions, hinting at a potential “fuel system 1 OL fault”. For example, you might notice:
- An Illuminated Check Engine Light: A clear indicator that something’s off-balance in your car’s system. The light typically comes on when the ECU has recorded a fault.
- Hesitation or Stalling during Acceleration: Deteriorated fuel system performance can lead to inconsistencies in delivering the proper fuel-air mix, causing your vehicle to hesitate or stall when accelerating.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Due to the fuel system operating in an ‘open loop’ status and relying on preset values, your car might consume more fuel than usual.
- Unsettling Smell of Fuel: A fuel system imbalance can result in the incomplete combustion of fuel, which could leave a noticeable smell in your car.
Reduced Vehicle Performance Indicators
Indications of reduced vehicle performance are critical flags that may suggest a “fuel system 1 OL fault”. Typically, you might experience:
- Decreased Power Output: A compromised fuel system can limit your engine’s power. You’ll find, especially during overtaking or uphill drives, that your car just doesn’t have the ‘get up and go’ it used to.
- Rough or Uneven Idle: Imbalanced fuel-air mix can upset the stability of your engine’s idle. This disruption might cause your car to shake or tremor when it’s not in movement.
- Difficulty Starting the Vehicle: Issues in the fuel delivery can extend the time required for successful ignition, making it challenging to start your car.
Profound recognition of these symptoms will help you discern when to consult a professional mechanic for a thorough vehicle check. Remember, timely detection and rectification of these faults uphold the vehicle’s performance while preserving its longevity.
Technical Explanation of Fuel System 1 OL Fault
Building on the previous section’s general description, let’s investigate deeper into what constitutes the “fuel system 1 OL fault,” how your car’s fuel system operates, and common malfunctions that contribute to this fault.
The Mechanism of Fuel Supply and Regulation
Your car’s fuel system serves an all-important function – it supplies and regulates fuel to the engine so your vehicle can operate efficiently. In a well-tuned car, a complex network comprising the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), sensors, and actuators collaborate to manage your fuel supply.
The fuel supply begins in the tank. As you depress the accelerator pedal, the throttle valve opens, signaling to the fuel pump to send fuel to the engine’s injectors. Simultaneously, the ECU, informed by input from the Oxygen (O2) sensors, adjusts the fuel injector duration to achieve the optimal air-fuel ratio. This ever-changing process, known as the closed-loop control system, relies on constant feedback from the O2 sensors.
Let’s consider the “Fuel System 1 OL fault.” The ‘OL’ stands for Open Loop, a reference to the control system’s operative mode. When your vehicle detects an issue that prevents it from adjusting the air-fuel mixture accurately, it jumps from a closed loop state to an open loop. Rather than using real-time data from the O2 sensors, the ECU refers to preset values to determine injector pulse width and air-fuel ratio. With this transition, fuel management deteriorates, potentially resulting in performance issues and higher emissions.
Common Malfunctions Leading to Fuel System Fault
Several malfunctions can prompt your vehicle to trigger the “Fuel System 1 OL fault” warning. Among the most common culprits are faulty O2 sensors and mass airflow sensors, and failed fuel injectors. O2 sensors monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gas and communicate this to the ECU, thereby playing a vital role in keeping the air-fuel mix balanced. If an O2 sensor fails, it leads to skewed data being sent to the ECU, nudging your vehicle into open loop mode.
Similarly, the mass airflow sensor, which measures the quantity of air entering the engine, can contribute to the fault if it malfunctions. Incorrect air measurements translate into incorrect air-fuel ratios, instigating the open-loop mode operation.
Also, problematic fuel injectors are a leading cause of fuel system faults. If an injector fails to spray the correct amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, the air-fuel mixture might lean out or flood, causing a variety of performance issues, including the triggering of the fuel system 1 ol fault.
In sum, any fault that disrupts the balance of the air-fuel mixture could push your vehicle into an open-loop state, leading to the onset of a “fuel system 1 OL fault”. An understanding of these processes and fault potential gives you the knowledge to identify when your vehicle might be signaling this particular issue.
Diagnosing Fuel System 1 OL Fault
When dealing with a Fuel System 1 OL Fault, diagnostic methods prove essential to gauge the problem’s nature. Let’s investigate into two dominant techniques, namely, using state-of-the-art automotive diagnostic tools and manual troubleshooting techniques.
Using Modern Automotive Diagnostic Tools
Modern automotive diagnostic tools provide a convenient and tech-savvy way to identify issues related to Fuel System 1 OL Fault. On-board diagnostic (OBD) scanners, for instance, connect directly to your vehicle’s onboard computer. Upon triggering the ‘Fuel System 1 OL Fault’ warning, these scanners read fault codes stored in your vehicle’s ECU. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) exact to Fuel System 1 OL Fault include P0171 and P0174, indicative of a engine running lean in Bank 1 and Bank 2, respectively.
Another critical tool is the multimeter, particularly when it comes to examining the electrical aspects of your vehicle’s fuel system. This versatile instrument measures voltage drops across different components, aiding in identifying malfunctioning elements such as faulty oxygen or airflow sensors.
Manual Troubleshooting Techniques
While advancements in technology offer important benefits, manual troubleshooting maintains its position as a reliable means of diagnosing Fuel System 1 OL Fault. Highlighting this approach is the method of physically examining essential fuel system components.
Start the inspection by checking your vehicle’s fuel injectors for clogs or leaks. A malfunctioning injector can disrupt the engine’s air-fuel mixture, leading to an open loop status. Similarly, gauge the condition of the vehicle’s fuel pump. Any impairment here may lead to an inadequate fuel supply, instigating the warning signal.
Another notable technique pertains to the examination of the engine’s vacuum lines. A vacuum leak can cause the engine to run lean, triggering the Fuel System 1 OL Fault. Hence, be sure to inspect these lines for any signs of wear or damage.
Remember, diagnosing a Fuel System 1 OL Fault doesn’t always demand professional aid. By grasping these diagnostic measures, you can take matters into your hands, ensuring effective vehicle management and, importantly, performance longevity.
Repairing and Preventing Fuel System 1 OL Fault
Let’s explore essential steps to repair the “Fuel System 1 OL Fault” issue and measures to prevent it from reoccurring.
Considerations Before Starting the Repairs
Addressing the ‘Fuel System 1 OL Fault’ requires certain pre-considerations. Firstly, ascertain that the severity of the fault isn’t beyond personal capabilities. If symptoms like incredibly rough idling, stalling, or a persistent smell of fuel, professional intervention could be required.
Next, verify if you’ve got proper tools available. Essential repair tools include an OBD II scanner for retrieving fault codes, a multimeter for checking electrical components, and a vehicle repair manual for referencing repair procedures exact to your model.
Another crucial consideration involves safety. Always disconnect the vehicle’s battery before beginning any repairs. It’s equally important to work in a well-ventilated area, particularly while dealing with fuel-related components to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes.
Step-by-step Repair Process
- Retrieve Fault Codes: Hook up the OBD II scanner to your vehicle’s OBD II port, usually found beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. Read and document the supplied fault codes.
- Inspect for Obvious Issues: Look for visible problems such as damaged hoses, noticeable leaks, or frayed wiring that could contribute to the fault.
- Check the Oxygen Sensors: Use the multimeter to inspect the oxygen sensors, ensuring they’re functioning as intended. If the multimeter displays irregular readings, consider replacing the sensors.
- Examine the Mass Air Flow Sensor: Assess the mass air flow sensor, responsible for determining the proper air-fuel mixture, for any potential faults.
- Test Fuel Injectors and Pump: Finally, test the fuel injectors and pump for adequate pressure and flow. If either component isn’t functioning correctly, replacement might be the best course of action.
Preventative Maintenance Measures
Preventing a ‘Fuel System 1 OL Fault’ involves regular monitoring and maintenance of your vehicle’s fuel system. Conduct routine checks on your vehicle’s oxygen and mass air flow sensors to ensure they’re accurately detecting and adjusting the air-fuel mixture.
Also, cleaning your fuel injectors periodically can prevent blockages or build-up that might pose operational issues. Regularly replacing your vehicle’s fuel filter, generally every 20,000 to 40,000 miles, also helps to keep the system functioning optimally.
Finally, staying alert to potential signs of a faltering system, such as reduced fuel economy, poor acceleration, or an illuminated check engine light, enables you to intervene before minor issues escalate into important faults. With these measures, you can securely maintain your vehicle’s fuel system and effectively prevent potential ‘Fuel System 1 OL Faults’.
Potential Impact of Fuel System 1 OL Fault on the Environment
Exploring into the environmental impact, a “fuel system 1 OL fault” can contribute significantly to a vehicle’s carbon footprint. This fault not only affects your car’s performance but also has environmental implications, particularly increasing harmful emissions.
How Faulty Systems Contribute to Increased Emissions
When a vehicle’s fuel system operates in an open loop, it largely ignores inputs from oxygen sensors. Instead, the Engine Control Unit (ECU) relies on default, pre-set fuel mixtures. This change in system operation tends to create more pollution. By running a richer air-fuel mixture – more fuel, less air – the car produces an excess of hydrocarbons (unburned fuel) and carbon monoxide. With the ECU unable to adjust the fuel mixture accurately, the combustion process becomes less efficient. This inefficiency translates to increased fuel consumption and so more greenhouse gas emissions. A faulty system disregards the vital feedback loop that ensures an efficient and clean-combustion process, illustrating how an unfixed “fuel system 1 ol fault” contributes to higher harmful emissions.
Action Towards Eco-friendly Vehicle Maintenance
To mitigate these negative environmental impacts, it’s vital to carry out eco-friendly vehicle maintenance tactics. Recognizing early signs of a potential “fuel system 1 ol fault” plays a crucial role in this. The moment your vehicle displays symptoms like hesitations during acceleration, poor fuel economy, or peculiar fuel smells, take proactive steps. Consult with an automotive professional or use diagnostic methods discussed earlier in the article. Implementing regular check-ups, standard upgrades, and timely repairs helps maintain your vehicle’s efficiency, reducing its environmental impact. For instance, monitoring the performance of sensors, keeping fuel injectors clean, and regularly replacing the fuel filter, are all proactive steps to help prevent faults like the “Fuel System 1 OL Fault.” Embracing these eco-friendly maintenance strategies supports both the longevity of your vehicle and the sustainability of our environment.
Conclusion
You’ve now got a comprehensive understanding of the “fuel system 1 ol fault”. You know it’s a warning about your vehicle’s fuel management system operating in an ‘open loop’. This can affect your car’s performance and increase emissions. You’ve learned the importance of recognizing the symptoms early, including a lit check engine light, stalling during acceleration, poor fuel economy, and a fuel smell.
You’re equipped with knowledge about how the fault occurs, and the diagnostic methods to identify it. Armed with tools like an OBD scanner and a multimeter, you can take proactive steps to manage your vehicle’s health.
You understand the importance of regular maintenance and timely repairs, not just to maintain your vehicle’s performance, but also to reduce its environmental impact. By addressing the “fuel system 1 ol fault” promptly, you’re not only ensuring a smooth drive, but also contributing to a greener planet. So, stay vigilant, stay informed, and drive safe.
What does it mean when you see “fuel system 1 ol fault” on your car’s dashboard?
The “fuel system 1 ol fault” warning signals a performance issue in the vehicle’s fuel management system. This fault is typically set off when the system goes into an ‘open loop’ state due to an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture. It is also indicative of possible efficiency issues and higher emissions.
How does the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’ affect a vehicle’s performance?
Any malfunction in the fuel system, as manifested by the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault,’ can disrupt the balance in fuel and air mixture, causing performance issues such as hesitation or stumbling during acceleration, poor fuel mileage, decreased power output, and difficulty starting the vehicle.
How can you diagnose the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’?
Diagnosing the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’ involves using automotive diagnostic tools like on-board diagnostic (OBD) scanners and multimeters. Manual inspection of fuel injectors, fuel pumps, and vacuum lines for potential clogs or leaks can also be helpful.
What are the steps to repair the ‘Fuel System 1 OL Fault’?
Fixing the ‘Fuel System 1 OL Fault’ begins with using an OBD II scanner to retrieve the fault codes and identify the problem accurately. Then, inspect the visible issues, check the oxygen and mass air flow sensors, and test the fuel injectors and pumps. Regularly cleaning fuel injectors and replacing the fuel filter can also prevent such faults from happening again.
How does the ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’ impact the environment?
The ‘fuel system 1 ol fault’ can increase a vehicle’s carbon footprint by leading to inefficient fuel combustion, resulting in higher emissions of harmful gases like hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. Therefore, it is critical to adopt eco-friendly vehicle maintenance practices, such as early fault detection and regular vehicle check-ups.
Related Posts:
- Deciphering the Honda B137 Service Code: A Guide for Every Honda Owner
- Decoding Honda B123 Service Code: Your Ultimate Guide to Better Vehicle Performance
- Unlocking the Mystery: Your Complete Guide to Honda’s B124 Service Code
- Deciphering Honda’s A13 Service Code: Maintenance Tips for Honda Owners
- Unraveling the Mystery: Your Complete Guide to Acura A13 Service Code
- Decoding the P1D73 Dodge Dart Issue: Comprehensive Guide to Navigate and Fix
- Mastering the C0561 71 Code: Essential Guide for a Smooth, Safe Drive
- Unlocking the Mystery: Understanding & Fixing the ECU 128 Code on Your Freightliner
- Decoding Your Car Dashboard: Unraveling the Fuel System 1 OL Fault Mystery
- Understanding STFT B1 Normal Range: Key to Optimal Vehicle Performance
- Understanding the ‘Service ESC’ Warning on Your Chevy Malibu: Safety, Diagnosis, and Maintenance